UART–TTL Debug Guide for NVIDIA Jetson

UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) is a widely used communication method that allows electronic devices to talk to each other by sending data one bit at a time. Developers often use UART to help debug their systems. By connecting a UART module to their device, they can send messages from the device to an external terminal or debugger. This makes it easier to watch what’s happening inside the system in real time — such as checking variables or seeing how the program is running. Because UART works asynchronously, it doesn’t need a shared clock signal between devices, which makes it relatively simple to use for debugging tasks.
Required Materials:
- NVIDIA Jetson Kits
- Jumper Cables
- FTDI or USB TTL Converter
- Native Ubuntu host computer
Connection
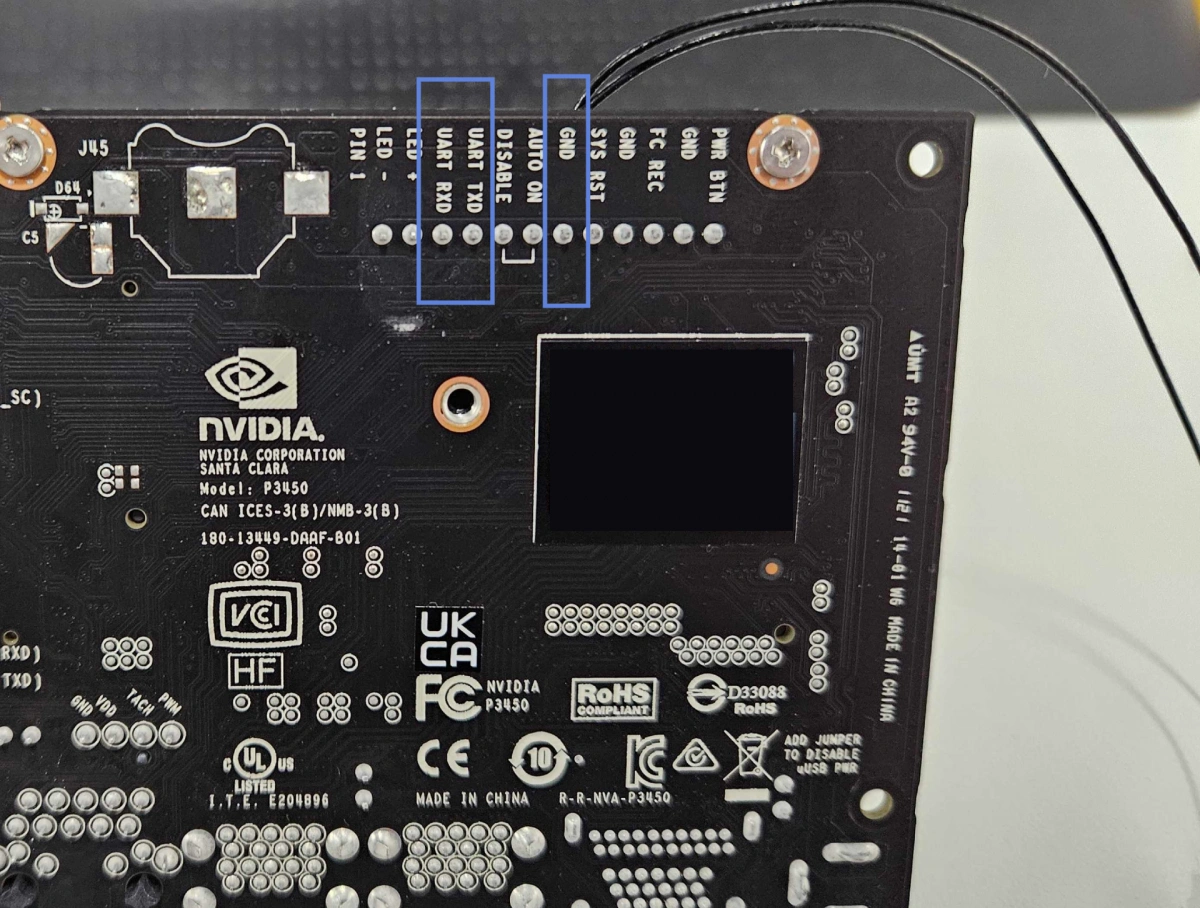
Identify the RXD, TXD, and GND pins on your FTDI or USB-TTL converter. You will use jumper wires to connect this module to your Jetson device. However, one important thing to note: the connections must be crossed. This means the TX pin from Jetson goes to the RX pin on the converter, and vice versa. You can follow the table below to correctly connect Jetson’s UART pins to the converter’s pins.
| Jetson | FTDI |
|---|---|
| RXD | TXD |
| TXD | RXD |
| GND | GND |
Next, connect the USB end of the converter to your computer. While making these connections, do not power on the Jetson yet. You will connect the power supply in Step 8.
Setup
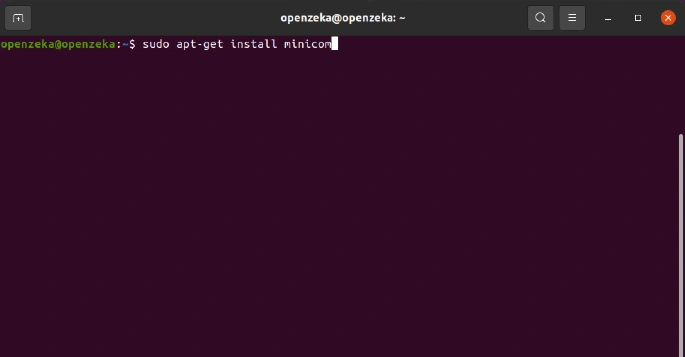
1. To perform debugging, we need an application called Minicom. You can install it by entering the following command in your computer’s terminal:
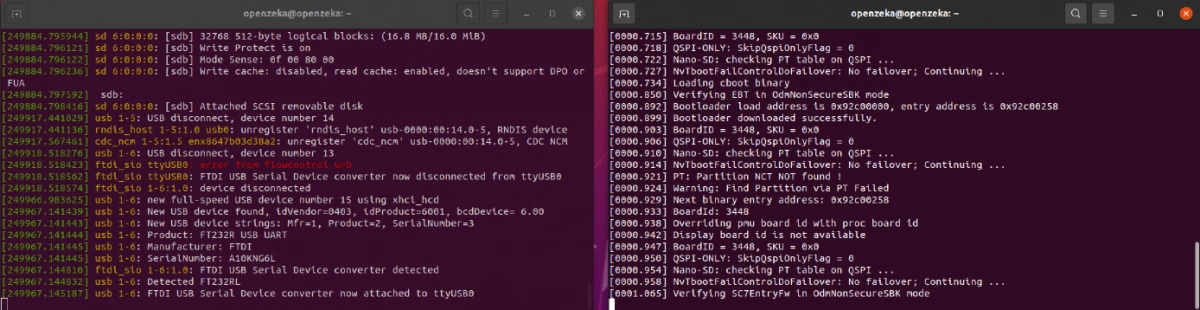
2. Another command we will use is dmesg, which stands for diagnostic messages. It shows system messages from the Linux kernel, such as those from device drivers.
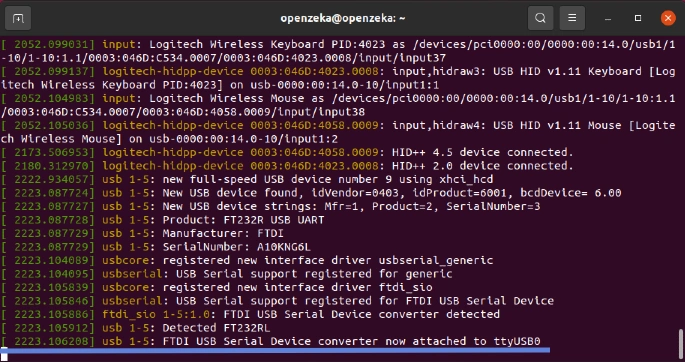
After running this command, plug in your USB converter to your computer. You will see a log appear in the terminal, similar to the image below.
In that log, the line that mentions FTDI refers to our USB converter, and ttyUSB0 is the port it is using. We will use this port name when setting up Minicom.
3. In this step, we will configure the Minicom application. Without closing the terminal window from the previous step, open a new terminal and enter the following command:
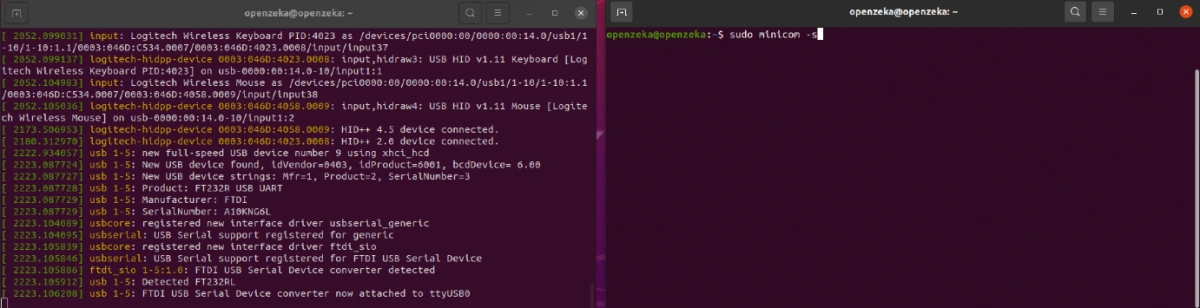
4. After starting Minicom, go to the “Serial Port Setup” option.
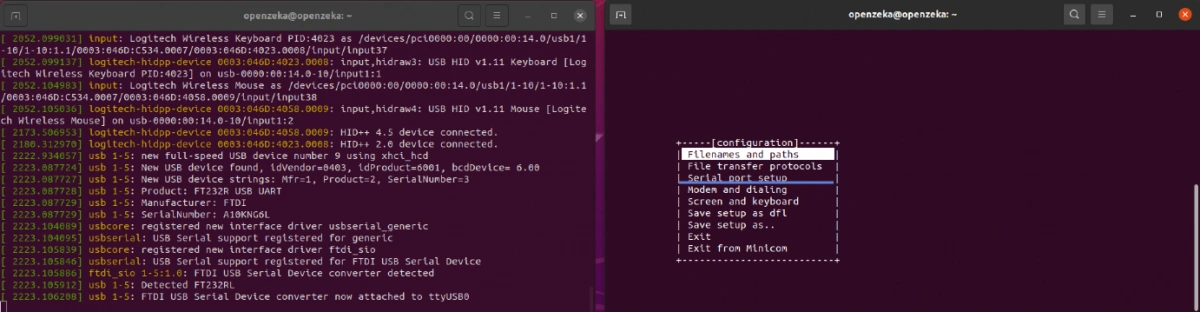
5. There are three important settings to check here; Serial Device, Bps/Par/Bits, and Hardware Flow Control.
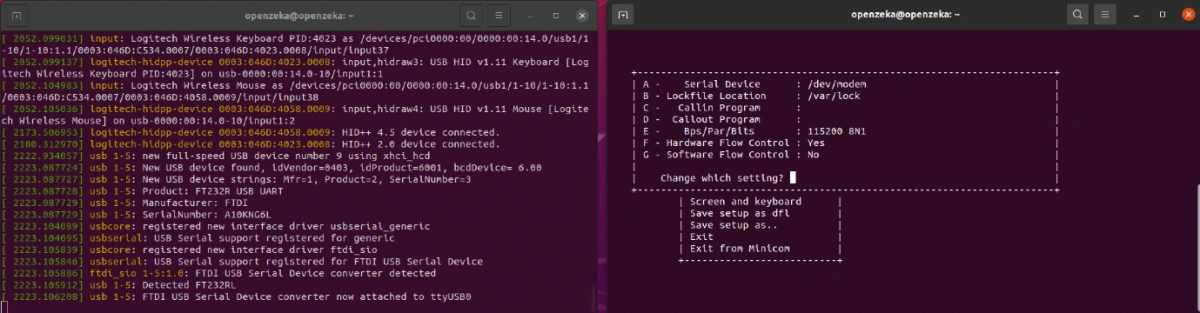
6. First, in the Serial Device section, enter the ttyUSB0 address you saw earlier in the dmesg –follow terminal.
Second, make sure the Bps/Par/Bits value is set to 115200 8N1. In our test, this value was set automatically, but if you see something different, change it to 115200 8N1.
Finally, the Hardware Flow Control option should be set to Yes.
Your final configuration should look like the example shown below.
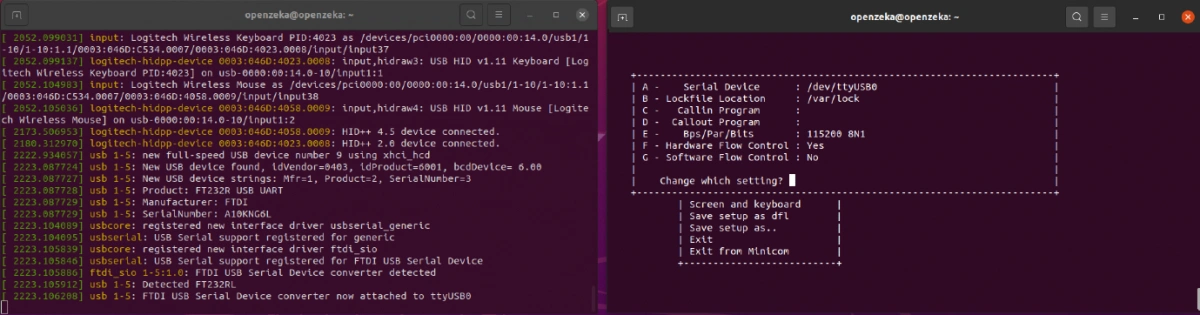
7. After completing Step 6, press the ESC key, then select “Save setup as dfl” to save your settings. After that, exit Minicom.
Now, open a new terminal and enter the command below. This time, you will see Minicom’s main interface.
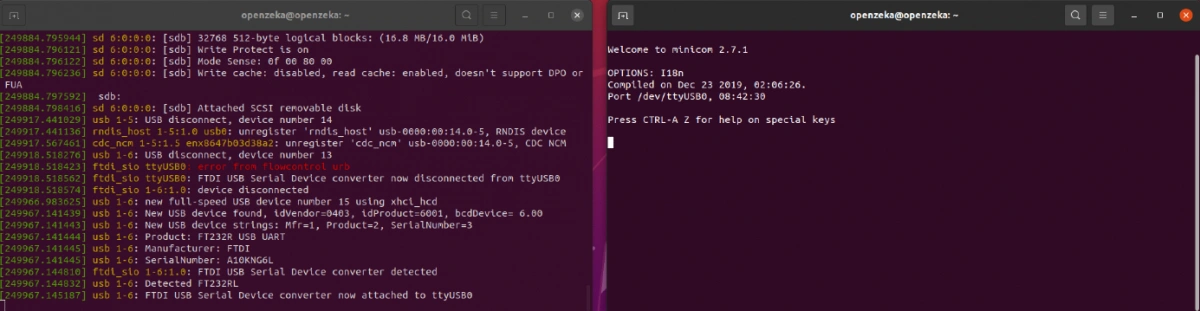
8. Now it’s time to power on your Jetson board. Once you connect the power, you will start to see messages appearing in Minicom.
When the boot process finishes, you can review the logs to check for any errors or important messages.